Freelancing offers flexibility and independence, but it also comes with unique responsibilities. One of the most important aspects of being a freelancer is understanding your tax obligations. Unlike traditional employees, freelancers must take charge of their own taxes, which can feel overwhelming at times. However, knowing what taxes to expect and how to prepare can make the process much smoother.
Different Types of Taxes Freelancers Need to Pay
Freelancers face several types of taxes that they need to account for when filing their annual returns. Here are the key taxes to keep in mind:
- Income Tax: This is the tax on your earnings. As a freelancer, your income tax rate will depend on your total taxable income.
- Self-Employment Tax: Freelancers are considered self-employed and must pay this tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare. The current self-employment tax rate is 15.3% on your net earnings.
- State and Local Taxes: Depending on where you live, you may also owe state and local taxes. Rates vary widely, so it’s important to check your local tax regulations.
- Sales Tax: If you sell goods or certain services, you may need to collect sales tax from your clients and remit it to your state.
Each of these taxes has its own rules and deadlines, so staying organized is essential.
Also Read This: How to Get a Job on Fiverr: A Comprehensive Guide
How Tax Rates Vary Based on Income Levels
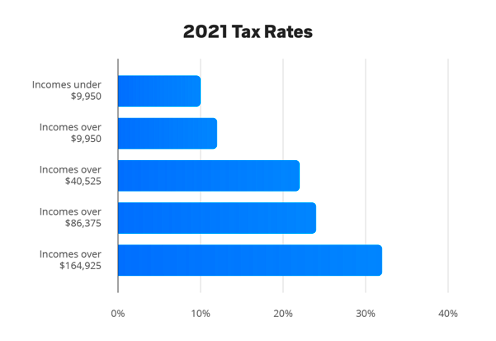
Tax rates for freelancers can vary significantly based on income levels. Here’s how it typically works:
The federal income tax system is progressive, meaning that the more you earn, the higher the rate you pay on your income. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $10,275 | 10% |
| $10,276 to $41,775 | 12% |
| $41,776 to $89,075 | 22% |
| $89,076 to $170,050 | 24% |
| $170,051 to $215,950 | 32% |
| $215,951 to $539,900 | 35% |
| Over $539,900 | 37% |
As your income increases, the percentage you pay in taxes also rises. This means that freelancers with higher earnings need to plan carefully for their tax obligations to avoid surprises when tax season arrives.
Also Read This: How to Check Your Sent Messages on Fiverr
Importance of Tracking Income and Expenses
As a freelancer, keeping track of your income and expenses is vital for managing your finances and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. It may seem tedious, but tracking these figures can save you money and help you avoid surprises when tax time comes. Knowing how much you earn and spend gives you a clearer picture of your financial health and can inform your future business decisions.
Here are a few reasons why tracking your income and expenses is essential:
- Accurate Tax Reporting: Keeping detailed records ensures that you report your earnings accurately, which is crucial for avoiding audits or penalties.
- Maximizing Deductions: By tracking your expenses, you can identify all the deductions you're entitled to, which can significantly lower your taxable income.
- Better Financial Planning: Knowing your income and expenses helps you budget effectively and plan for leaner months.
- Understanding Profitability: Regular tracking helps you evaluate which projects or clients are most profitable, guiding your business strategy.
Consider using accounting software or a simple spreadsheet to keep everything organized. Make it a habit to update your records regularly, and you’ll find tax season a lot less stressful!
Also Read This: Is It Free to Sell on Fiverr? A Comprehensive Guide
Common Deductions Freelancers Can Claim
Freelancers are often eligible for a variety of tax deductions that can help lower their taxable income. Understanding these deductions is key to maximizing your savings. Here are some common deductions freelancers can claim:
- Home Office Deduction: If you work from home, you can deduct a portion of your rent or mortgage, utilities, and other related expenses based on the size of your workspace.
- Supplies and Equipment: Costs for items like computers, software, office supplies, and other necessary equipment are deductible.
- Business Travel Expenses: If you travel for work, you can deduct expenses such as airfare, hotels, meals, and transportation.
- Marketing and Advertising: Any costs associated with promoting your freelance business, like website development or advertising, can also be deducted.
- Professional Services: Fees paid to accountants, consultants, or legal advisors for your business are deductible.
Always keep receipts and records of your expenses to support your claims. Knowing what you can deduct can significantly reduce your tax burden and keep more money in your pocket.
Also Read This: Per Word Rates for Freelance Writing
Filing Taxes as a Freelancer
Filing taxes as a freelancer can seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. With the right approach and preparation, you can navigate the process smoothly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through it:
- Gather Your Documents: Collect all relevant documents, including income statements, expense receipts, and any 1099 forms you received from clients.
- Calculate Your Income: Add up all your income from freelance work. Be sure to include any side gigs or additional income streams.
- Deduct Expenses: Subtract your total business expenses from your income to find your net earnings. This amount is what you will be taxed on.
- Complete the Right Tax Forms: Use IRS Form 1040 and Schedule C to report your income and expenses. If your net earnings are $400 or more, you will also need to file Schedule SE for self-employment tax.
- Consider Estimated Taxes: If you expect to owe $1,000 or more in taxes, make quarterly estimated tax payments to avoid penalties.
- File Before the Deadline: Be sure to submit your taxes by the deadline to avoid late fees. Typically, this is April 15th for most freelancers.
If you're unsure about the process, consider consulting with a tax professional who can guide you. With preparation and organization, filing your taxes can be a straightforward task.
Also Read This: How to Post a Gig on Fiverr: A Step-by-Step Guide
Estimated Tax Payments and Their Significance
For freelancers, understanding estimated tax payments is crucial. Unlike traditional employees who have taxes withheld from their paychecks, freelancers must pay taxes on their income throughout the year. This means you need to estimate your tax liability and make payments quarterly. This system helps you avoid a hefty tax bill come April and potential penalties for underpayment.
Here are some important points about estimated tax payments:
- Quarterly Payments: Generally, you need to make estimated payments four times a year. The typical schedule is April 15, June 15, September 15, and January 15 of the following year.
- Calculate Your Payment: To determine how much you should pay, you can estimate your expected income for the year and apply the appropriate tax rates. Alternatively, you can base it on the previous year’s income if your earnings are similar.
- Use IRS Form 1040-ES: This form helps you calculate your estimated taxes and provides payment vouchers for each quarter.
- Avoiding Penalties: If you expect to owe $1,000 or more when you file your tax return, making estimated payments can help you avoid underpayment penalties.
Staying on top of your estimated tax payments keeps your finances organized and prevents any surprises when tax season arrives.
Also Read This: Earnings Potential for Freelance Coders in the Modern Market
FAQ About Taxes for Freelancers
Freelancers often have questions about their tax responsibilities. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify common concerns:
- Do freelancers pay self-employment tax? Yes, freelancers are responsible for paying self-employment tax, which covers Social Security and Medicare.
- How can I reduce my taxable income? You can lower your taxable income by claiming all eligible deductions, such as business expenses, home office costs, and health insurance premiums.
- What if I can’t pay my taxes on time? If you can’t pay your taxes by the deadline, file your return anyway to avoid a failure-to-file penalty. Then, explore options like payment plans with the IRS.
- Is it better to hire a tax professional? It can be beneficial, especially if your finances are complicated. A tax professional can help you maximize deductions and navigate tax laws.
- What records should I keep for tax purposes? Keep records of all income and expenses, receipts, invoices, and any tax documents like 1099 forms for at least three years.
Addressing these common questions can help ease your worries and prepare you for tax season.
Conclusion on Tax Responsibilities for Freelancers
Understanding tax responsibilities as a freelancer is essential for your financial health and peace of mind. While navigating taxes can seem complex, staying organized and informed can simplify the process. From tracking your income and expenses to knowing the deductions available, each step plays a critical role in your overall financial strategy.
Remember to keep detailed records, make estimated tax payments, and consider seeking professional advice when needed. By taking these proactive steps, you can minimize your tax liability and ensure compliance with tax laws. Freelancing can be a rewarding career, and managing your taxes effectively allows you to focus more on your work and less on financial worries.
In the end, being knowledgeable about your tax obligations will help you thrive as a freelancer. Stay informed, plan ahead, and you’ll navigate tax season with confidence.




